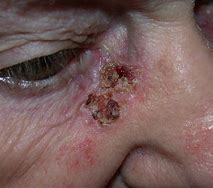
Basal Cell Cancer
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, is the most common type of skin cancer.
It often appears as a painless raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it; or it may present as a raised area with ulceration.
Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it but is unlikely to spread to distant areas or to result in death.
Causes
Risk factors include :-
- Exposure to ultraviolet light
- Having lighter skin
- Radiation therapy
- Long-term exposure to arsenic
- poor immune-system function
Exposure to UV light during childhood is particularly harmful.Tanning beds have become another common source of ultraviolet radiation.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis often depends on skin examination, confirmed by tissue biopsy.
It remains unclear whether sunscreen affects the risk of basal-cell cancer.
Treatment is typically by surgical removal.This can be by simple excision if the cancer is small; otherwise Mohs surgery is generally recommended.
Other options may include application of cold, topical chemotherapy, laser surgery, or the use of imiquimod.
In the rare cases in which distant spread has occurred, chemotherapy or targeted therapy may be used.
Basal-cell cancer accounts for at least 32% of all cancers globally. Of skin cancers other than melanoma, about 80% are basal-cell cancers.
In the United States about 35% of white males and 25% of white females are affected by BCC at some point in their life.
Other types are......................................
Index
